Reading: Here is a list of sections in the text which I will be assuming you have some familiarity with: Chapter 1, 2.1-5, 2.7, 2.9-11, 3.1-3, 4.1, 4.4, 5.1-7, 15.1-4, 16.1-16.10, 17.1-17.7, 19.1-19.6, 19.8, 20.1-3, 21.1, 26.1-2, 27.1-3, Appendix A
Subject of this course:
Additive errors:
Assume
![]() (or define
(or define
![]() and deduce that
and deduce that
![]() ).
).
For a sample of size n:
Goal now: relate ![]() to ``conditions'' for measurement i.
to ``conditions'' for measurement i.
``Condition'' summarized by values of ``covariates''
Often we assume
Key is:
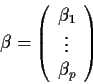
A useful alternative description:
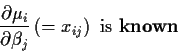
Thermoluminescence (TL) dating can be used to determine how old a piece of pottery is or how old a sand dune is. When a piece of pottery is found by an archaeologist it is ground up and split into small samples. The samples are irradiated with different amounts of gamma radiation and then heated in an oven. At temperatures around 300 Celsius they glow with blue light called thermoluminescence. The amount of light given off, Y depends on the dose D of radiation given by the analyst (and also on the amount of radiation --cosmic rays or radiation from trace isotopes in the ground-- to which the pot or sand was exposed while buried).
Several models are in use:
Of these the first three are linear models while the fourth is not. In the
first three cases the mean ![]() can be differentiated with respect to
any
can be differentiated with respect to
any ![]() and you get a known (measured) constant.
Thus for example in the second model
and you get a known (measured) constant.
Thus for example in the second model
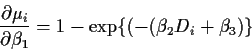
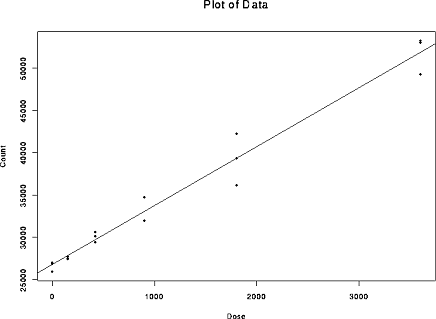
Here is a plot of the data with the least squares line drawn in.
Here is the same plot with the least squares fit of the quadratic model.
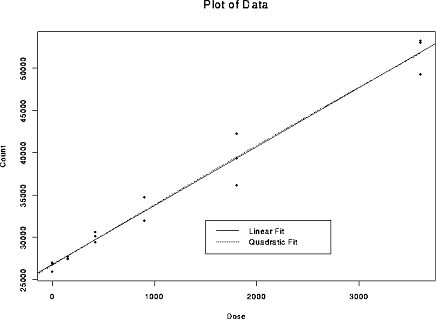
You will see that the two fits are virtually indistinguishable.
In this course we will want to test the hypothesis that the ![]() term in the quadratic model can be left out. To see the importance of this
consider the use to which these models are put. Physicists reckon that the
intercept term
term in the quadratic model can be left out. To see the importance of this
consider the use to which these models are put. Physicists reckon that the
intercept term ![]() which is the amount of TL if you don't add
any radiation is the TL due to the exposure to cosmic rays and so on
while buried. The total exposure while buried is equivalent to some
dose Deq of added radiation called the ``equivalent dose'',
equivalent in the sense that
which is the amount of TL if you don't add
any radiation is the TL due to the exposure to cosmic rays and so on
while buried. The total exposure while buried is equivalent to some
dose Deq of added radiation called the ``equivalent dose'',
equivalent in the sense that
![]() if a
straight line model is appropriate. This dose is measured by finding the value
of D which would produce a predicted TL equal to 0, that is,
by extending the graph to negative doses until the fit crosses the x axis.
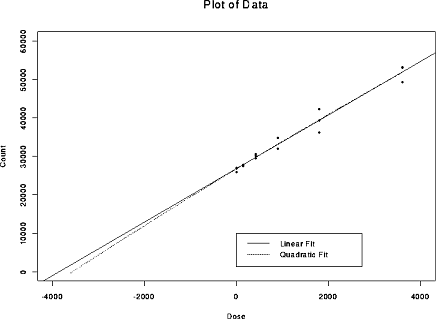
In the next plot
you can see that the linear and quadratic fits do cross the x axis (or y=0)
at different places.
if a
straight line model is appropriate. This dose is measured by finding the value
of D which would produce a predicted TL equal to 0, that is,
by extending the graph to negative doses until the fit crosses the x axis.
In the next plot
you can see that the linear and quadratic fits do cross the x axis (or y=0)
at different places.
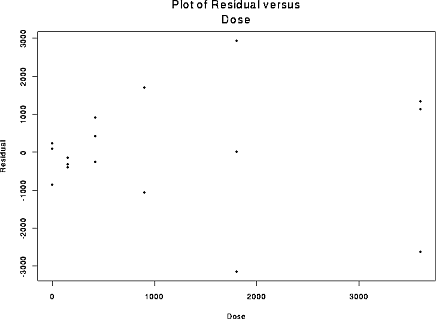
We will be fitting linear models (and near the end of the course non-linear models like the saturating exponential) by least squares. We will examine residual plots to judge whether or not the model assumptions are adequate:
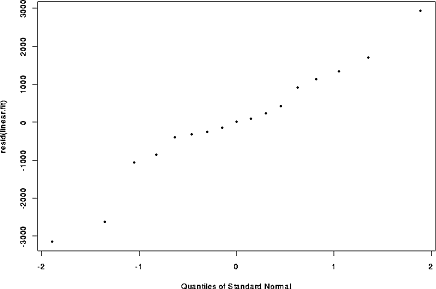
We will look at Q-Q plots of the residuals to judge normality.